furuncle of olboul treatment in Kabul
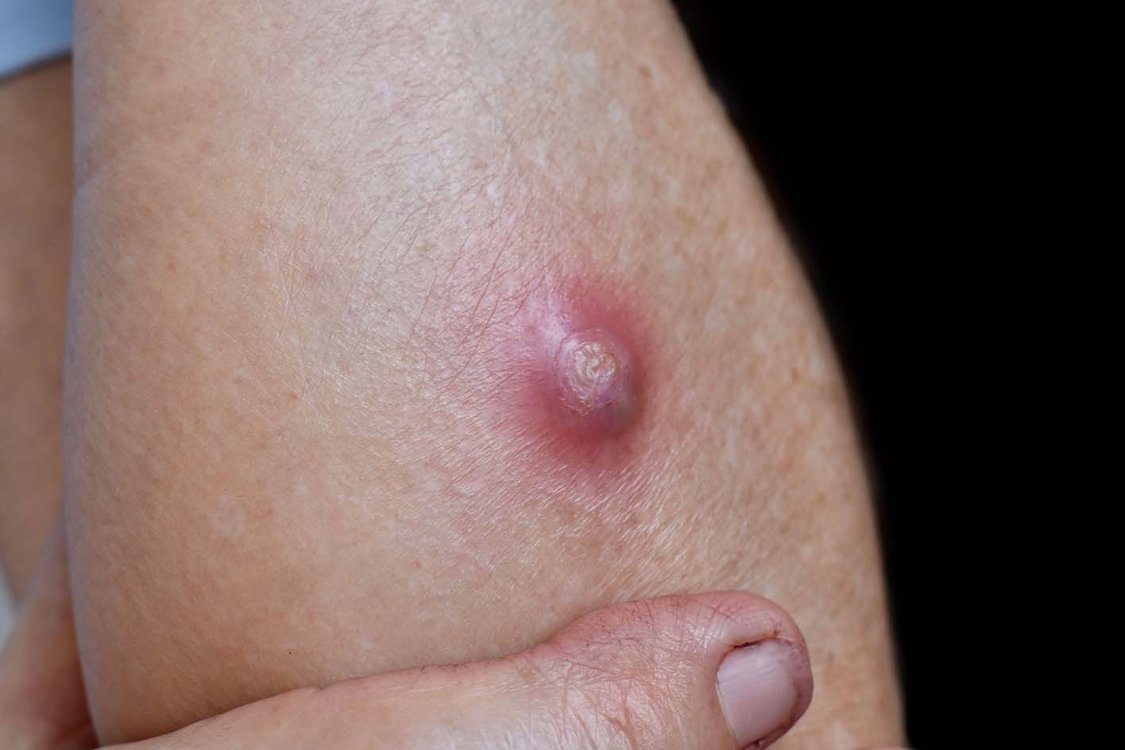
What is a Boil (Furuncle)?
A boil, also known as a furuncle, is a type of deep folliculitis, a bacterial infection of the hair follicle. This condition occurs when bacteria enter the deeper parts of the hair follicle, leading to inflammation and infection.
Characteristics of a Boil
A boil typically appears as one or more red, painful, raised, and pus-filled lumps on the skin. Upon close examination, you will notice that the boil is centered around a hair follicle. It often starts as a small, painful pimple, growing larger and more painful over time. Eventually, a larger bump forms with a central opening from which white pus is expelled. Once the pus drains, the pain decreases, and the wound gradually heals. When multiple boils occur in a cluster, it is called a carbuncle. Larger boils may develop into an abscess, which is defined as the accumulation of pus beneath the skin and muscles. In some cases, cellulitis can occur, meaning the bacteria spread to the surrounding skin and tissue, causing redness, swelling, and pain. This can also lead to fever and malaise.
Why Do Boils Develop?
Most people who get boils are otherwise healthy and practice good personal hygiene. However, they carry the Staphylococcus aureus bacteria on the surface of their skin (known as being a staph carrier). The exact reason why this happens is often unclear, but it is estimated that 10-20% of people are carriers of staph. Staphylococcus aureus commonly resides in the nose, armpits, groin area, and buttocks, and can spread to other areas of the body via fingernails. Small scratches, minor skin abrasions, or friction can introduce these bacteria into the wall of a hair follicle, making it vulnerable to infection. Once infected, the boil goes through its typical course, which usually lasts around 10 days.
Although most people with boils are healthy, sometimes boils are associated with a weakened immune system, diabetes, smoking, or iron deficiency.
How to Treat a Boil?
Treatment for a boil depends on its severity. Your doctor may provide you with specific medical advice and treatments. Here are some common treatments for boils:
- Use of antiseptic soap or antibacterial soap during daily showers for at least one week, followed by use two times a week for several weeks.
- Regularly apply hand sanitizer to reduce the risk of re-infection or spreading infection to others through contaminated hands.
- Topical antibiotic ointments or gels for application inside the nostrils.
- Cleanse your entire skin surface with 70% isopropyl alcohol for one week. Afterward, apply vaseline to your skin to prevent dryness.
- Topical antiseptics such as povidone-iodine or chlorhexidine cream should be applied directly to the boil and covered with a gauze square.
- Your doctor may prescribe an oral antibiotic (usually penicillin or flucloxacillin) for several weeks if necessary.
- Family members who are also affected by boils should follow the same skin-cleansing regimen.
- If Staphylococcus aureus is present, your doctor may recommend applying a topical antibiotic to the nostrils of family members to prevent spreading.
- If boils do not resolve, swabs may be taken to test for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).
- Occasionally, your doctor may prescribe specific antibiotics such as fusidic acid, clindamycin, rifampicin, or cephalosporins based on your condition.
General Measures to Prevent Boils:
- Consult your doctor about your overall health.
- If you are overweight, consider losing weight. Regular exercise is essential.
- Follow a healthy diet, including meat, lots of fruits, and vegetables.
- Avoid smoking to improve your immune system and skin health.
- Shower daily with soap or a cleanser, and wash your hands multiple times a day or use hand sanitizers.
- Do not share personal items such as towels or razors.
- Use a clean tissue and avoid touching or scratching your nose.
- Change your underwear and nightwear regularly.
- Engage in activities that minimize skin friction, such as low-impact sports or jogging.
- If you suffer from iron deficiency, taking iron supplements may help reduce the risk of infection.
- Vitamin C (1000 mg daily) has been shown to improve neutrophil function, supporting your immune system.
For further information on boils and their treatment, feel free to contact Arvin Skin Hospital for a consultation and personalized advice. Whether you need treatment for a skin infection or help with a persistent boil, we offer expert care for all your dermatological needs.
